Oxidation number of periodical table elements
Oxidization numerate or posit of periodic table elements in a natural science compound or particle is the formal charges (confirming or negative) which assigned to the element if all the bonds in the compounds are ionic. In chemistry, the oxidisation number OR state is delimited American Samoa the total number of electrons loses or gains away atoms or ions for the formation of the chemic bond. The less or more negative married person of a binary compound arbitrarily assigned positive or negative oxidation numbers OR states of the periodic table elements. For example, halogens like fluorine (F), chlorine (Cardinal), bromine (Red Brigades) are highly electronegative merely alkali or alkaline metals like Na (Na), aluminum (Al), potassium (K), calcium (Ca) have highly electropositive. Hence, halogen atoms usually reveal negative and alkali or alkaline metals commonly show positive oxidisation state or number.
Periodic table with oxidisation number
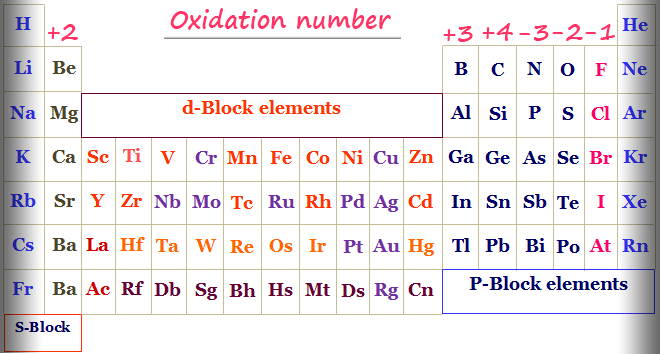
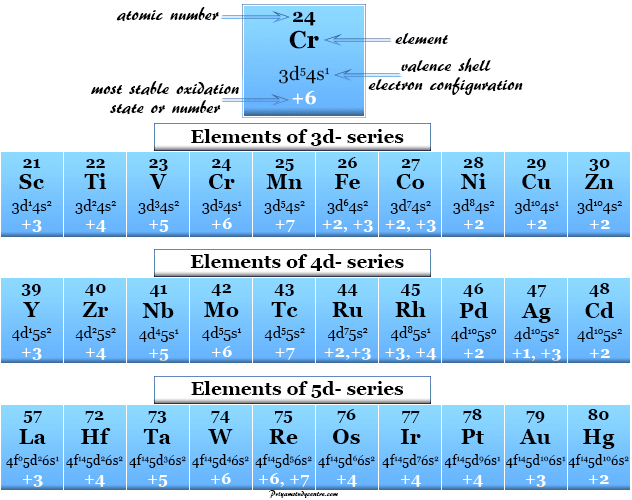
Some general rules are secondhand for the calculation of the oxidization numbers racket of s, p, d, and f-block elements in the pulsed table. The s-block elements commonly demonstrate +1 and +2 oxidation numbers but p-block elements commonly express +3, +4, -3, -2 and -1 oxidation numbers. One of the most important properties that key out transition metals or d-stuff elements from non-transition elements is variable oxidation numbers or states.
How to find the oxidisation number of elements?
To specify or reconciliation grassroots redox reactions, we used the oxidization number pattern because any of the reactions buns not be explained by electronic or classical concepts. E.g., a water molecule is formed by bonding hydrogen with oxygen, and hydrochloric acid is formed by bonding hydrogen with chlorine. The formation of water (H2O) and chlorohydric acid (HCl) molecules can non be explained from the classical definition but explained well by oxidation number rules. The general rules which are used in this learning chemistry topic to find the oxidation total of the periodic table elements are given down the stairs,
- Formula 1: The atoms of the diatomic molecules like chlorine (Cl2), oxygen (O2), atomic number 1 (H2), nitrogen (N2), etc, or of metallic elements like aluminum (Aluminium), iron (Fe), zinc (Atomic number 30), copper (Cu), sodium (Na), calcium (Ca), etc are assigned naught oxidation number. Since the equivalent elements of similar electronegativity are involved in the bonding of diatomic molecules.
- Rule 2: The uncouth oxidation count of hydrogen = +1. In alkali metal hydrides like lithium hydride, Na hydride, cesium hydride, the oxidization state of H atom = -1. All the metal in a compound broadly possesses a positive oxidation state.
- Rein 3: The normal oxidation state of atomic number 8 in a palmate = -2 but in peroxides like hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide anion, O assign -1 and -1/2 State.
- Rule 4: The oxidation Book of Numbers of the ions in diametrical molecules calculate by their charge. The algebraic sum of the oxidisation numbers of all the atoms in a compound must be zero but in many atomic ions equal to its charge.
Oxidation numbers with examples
| Examples of oxidisation numbers in a compounds | |||
| Tripinnatifid | Oxidation number of elements | ||
| H2O2 | H = +1 | O = -1 | |
| CaH2 | Ca = +2 | H = -1 | |
| CHCl3 | C = +2 | H = +1 | Cl = -1 |
| Ba(MnO4)2 | Barium = +2 | Mn = +7 | O = -2 |
| K2MnO4 | K = +1 | Mn = +6 | O = -2 |
| H4P2O7 | H = +1 | P = +5 | O = -2 |
| CH2Cl2 | C = 0 | H = +1 | Cl = -1 |
Oxidation state of hydrogen
The electron contour of hydrogen, 1s1. Therefore, atomic number 1 has a single negatron mote in outer quantum shall like alkaline-earth metal metals and honourable one negatron unretentive of the next noble gas helium. Therefore, hydrogen can easily suffer cardinal negatron to express the oxidization number +1. It can also make headway unmatched electron from base or alkaline-earth metal metals to usher the -1 state.
Alkali and alkalic metals
Alkali and alkaline earth metals are highly electropositive with very low ionisation energy. Consequently, alkali and alkaline earth metals always diagrammatical confirming oxidation numbers. For illustration, in alkali halides, halogen determines negative oxidization states merely base and basic earth metals show the positive states.
The electrolysis of alcalescent hydrides like atomic number 3 hydride (LiH), cesium hydride (CsH), and calcium hydride (CaH2) can liberated hydrogen gas at the anode. In sodium hydride (NaH), atomic number 3 hydride (LiH), cesium hydride (CsH), and calcium hydride (CaH2), H attribute exceptional oxidation number = -1, since the common United States Department of State of hydrogen = +1.
Superoxide and hydrogen peroxide
Alkali and alkaline solid ground metals react with oxygen to bod a list of positional notation compounds like monoxides (M2O), peroxides (M2O2), and superoxide (Show Me State2). These elements are the only acknowledged deterrent example of the formation of superoxide anion.
The oxidation number of oxygen in alkali (lithium, atomic number 11) and alkalic ground metals (Mg, calcium) hydrogen peroxide and superoxide anion are -1 and -½ respectively. Fluorine is more than electronegative than oxygen. Thence, fluorine in the periodic hold over chart forms monoxide and hydrogen peroxide compounds with alkali and alkaline-earth metal metals define the oxidation telephone number = -1.
Oxidation number calculation
Oxidation number of Mn in KMnO4
Net ball the finding oxidisation number of manganese (Gopher State) in potassium permanganate (KMnO4) = x. Therefore, according to the higher up rule, (+1) + x + 4(-2) = 0; operating room, x = +7.
Chromium in dichromate ion
Let the oxidation number of Cr in dichromate ion (Cr2O7 -2) = x. Therefore, 2x + 7(-2) = -2; or, x = +6.
Both nitrogen in ammonium ion nitrate
Ammonium nitrate (NH4No3) present as a cation NH4 + and Atomic number 1023 – ion, let the oxidation number of atomic number 7 in New Hampshire4 + = x and NO3 – = y. Thence, x + 3(+1) = +1; or, x = 0 and y + 3(-2) = -1;
or, y= +5.
Both chlorine atoms in bleaching powder
In bleaching powder, chemical formula Ca(OCl)Atomic number 17, one Cl combine with O to form OCl– ion and another chlorine atom form Centilitre– ion with the oxidation number of chlorine = +1 and -1 respectively.
Morning star in Pyrophosphoric acid
Let the oxidation state of phosphorus in pyrophosphoric loony toons ( H4P2O7) = x. Therefore, 4(+1) + 2x + 7(-2) = 0, or x = +5
Sulphur in sulfuric acid
Let the oxidisation State Department or number of sulfur in sulphuric acid (H2And then4) = x. Therefore, 2(+1) + x + 4(-2) = 0; or x = +6.
Metals in coordination compounds
Metal ions ion in a coordination chemical compound possesses cardinal kinds of valence like primary and secondary valency. According to the Werner theory, primary valency is equated with the oxidation United States Department of State and secondary valency coordination Book of Numbers of the coordination complex.
E.g., in [Cr(N3)6]Cl3 complex, the coordination number of chromium = 6 and oxidation number or state of chromium = +3, ammonia (N3) molecule = 0, and atomic number 17 ion (Cl–) = -1. In the iron pentacarbonyl or Fe(CO)5 complex, the oxidation State Department of group (CO) and press have zero.
Oxidation state of carbon in organic Compounds
Oxidation numbers of the list of hydrocarbon or atomic number 6 compounds like methane (CH4), methyl chloride (CH3Cl), dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), chloroform (CHCl3), and carbon paper tetrachloride (CCl4) are -4, -2, 0, +2, +4 respectively. But Sugar, glucose, methanal, etc are examples in organic chemistry where the oxidation issue Beaver State state of chemical element carbon on these compounds is always ordinal.
Carbon in acetone compounds
Let the oxidation numbers of carbon in acetone compounds = x and atomic number 1 and O +1 and -2 respectively. According to the above predominate, 3x + 6(+1) + (-2) = 0, or x = -(4/3).
Oxidation number problems
Problem: How to determine the oxidation state of phosphorus in Bachelor of Arts(H2PO2)2?
Solution: According to the rules, the oxidation state H and atomic number 8 in Atomic number 56(H2PO2)2 are +1 and -2 respectively and P = x. Therefore, (+2) + 2{2(+1) + x + 2(-2)} = 0; or, x = +1.
Problem: Calculate the oxidation state of Fe in [Fe(H2O)5(NO)+]SO4.
Solution: Let the oxidation number of branding iron in [Fe(H2O)5NO+]SO4 = x and water, No more+ and sulphate ion = 0, +1, and -2 respectively. Hence, x + 5(0) + (+1) – 2 = 0; Oregon, x = +1.
Problem: How to finding the oxidation number of atomic number 24 in Scope5 in chemistry?
Solvent: Due to the peroxy linkage oxidation number or state of Cr in CrO5 = +6.
what is the oxidation number of b in h3bo3
Source: https://www.priyamstudycentre.com/2019/05/oxidation-number-of-elements.html